Terpenes are responsible for the scent of essential oils. For centuries, they have been used in aromatherapy to promote emotional and physical well-being. But beyond their role in producing aroma, they are also recognized for other health benefits. To better understand the nature of these compounds, let’s look at some essential information about them.
What are terpenes, exactly?
Terpenes are naturally occurring organic compounds found in plants and some animals. They are what give plants and trees their smell, flavors, and even colors. According to scientists, there are over 20,000 different terpenes but they have studied only a handful out of this number.
While nearly all plants contain terpenes, some of the more common sources include tea, citrus fruits, and herbs like sage, thyme, rosemary, and mint.
What do they do?
Terpenes play a key role in plants, helping them recover from damage by acting as part of their immune system to keep away infectious germs. In most cases, terpenes attract pollinators, enabling the plants to produce seeds and fruits. Their strong scent also repels predators like insects and foraging animals.
In the industrial setting, manufacturers use terpenes to create the flavors and scents of many everyday products such as perfume, cosmetics, and even foods. They are also processed into home care substances such as cleaning solvents, pesticides, and varnishes.
What are their effects on humans?
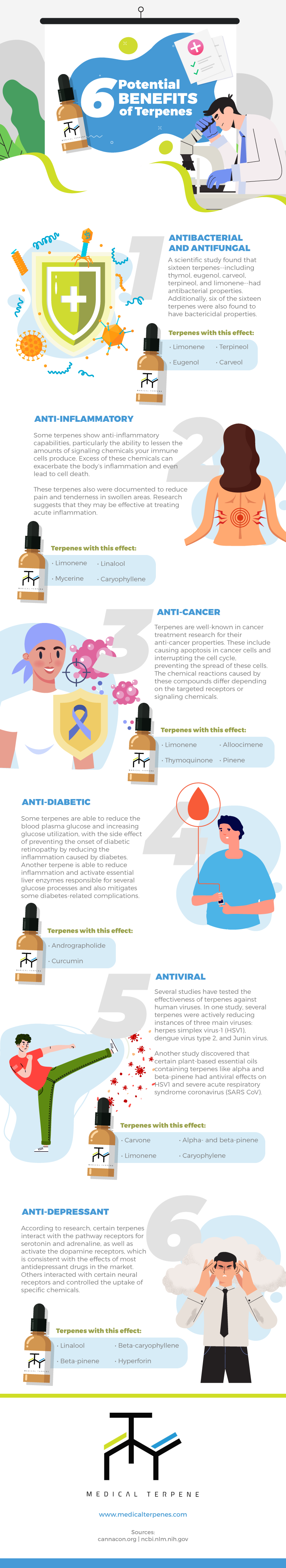
Certain terpenes have been widely used in natural folk medicine for various applications. One such terpene is curcumin has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, and antiseptic properties.
Several studies have also established the link between certain types of terpenes and their health benefits. For instance, myrcene has been found to exhibit antibiotic, anti-inflammatory, and sedative properties. Meanwhile, linalool has been shown to have antimicrobial, anticancer, and antioxidant effects.
- Antifungal / Antibacterial
Antibacterial, antifungal, and antimicrobial activities of terpenes have been discovered in a number of researches.
The study discovered antibacterial effects in sixteen terpenes, including thymol, eugenol, carveol, terpineol, and limonene. Eugenol was one of two terpenes that inhibited bacterial growth the most effectively.
- Anti-inflammatory
Some terpenes have anti-inflammatory properties, including the potential to reduce the number of signaling chemicals produced by your immune cells. Excessive concentrations of signaling substances in the body might induce excessive inflammation and eventually cell death.
These terpenes also had pain-relieving properties, such as reducing discomfort in swollen areas. Terpenes have shown to be particularly effective in pain reduction in both in vitro and in vivo studies in research of terpenoid-rich essential oils. According to the findings, these chemicals can be employed to treat acute inflammation rather than chronic inflammation.
- Anti-cancer
Terpenes are well-known for their anti-cancer properties in cancer treatment studies. Cancer cells are subjected to apoptosis and the cell cycle is disrupted, preventing them from multiplying. Depending on the targeted receptors or signaling substances, these chemical processes can vary significantly.
While terpenes are used in different ways in different trials, they have been demonstrated to be effective against a variety of cancers. Cancers of the colon, brain, prostate gland, bone, lungs, breast, and skin are among them.
The infographic below will help you get a better glimpse of the medical benefits of terpenes, including the specific types of terpenes that exhibit them.